East Side Story: The Made-For-Hollywood Tale of a 16-Year Legal Tussle to Help a Dedicated Band of Manhattan “Homesteaders” Take Ownership of the Building They Had Moved Into And Begun to Rehab

By Best Lawyers
Last year, Ramin Bahrani, one of my clients, was nominated for an Academy Award for Best Adapted Screenplay. For his previous movie, 99 Homes (2015), I had helped script the court scenes and advised closely on the script overall. I reminded Ramin that no real estate attorney had ever been thanked onstage by an Oscar winner. In my humble opinion, that streak was primed to end—we “dirt lawyers” have exciting, compelling stories to tell. That goes double for me, a small-firm lawyer. Though guidance on a screenplay helped Ramin, it’s the legal assistance I’ve given to one very prominent actress and her family that is part of my real-life work. This is the tale.
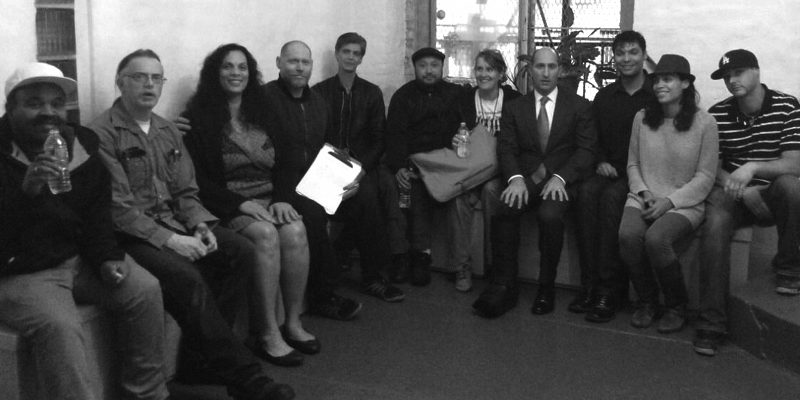
Shortly after starting my own firm, I was hired by several building squatters. That’s how they referred to themselves, anyway. They had broken into abandoned buildings on the Lower East Side of Manhattan and made them livable enough for small groups. In one six-story building, 544 East 13th Street, all these homesteaders—I banned the word squatter shortly after starting work with them, as they had a right to be living there—brought certain skills to bear. They did their own electrical work, pirating power from the light post on the sidewalk out front. They opened a bank account so they could obtain a water meter. They installed carpeting and pipes, made water run through those pipes and put in one refrigerator and one light bulb per floor.
The city had initially determined that the 13th Street building and others around it should be demolished, so the homesteaders had to fend off foreclosure. Later, though, city officials offered them the chance to buy the building for $1 if they would restore it to a legal residence and learn how to run it with a nonprofit organization that couldn’t run its own affairs.
I was handling all sorts of legal affairs for many of these buildings, as it seemed that the people at the agency that was supposed to be their caretaker were more interested in taking over the buildings altogether. I won several small battles in court, and eventually we sued the caretaker organization for theft and mismanagement, demanding that they cede ownership of the 13th Street building to the homesteaders.
The caretaker group was shocked and angry at being held accountable—but it forced them to get their act together and begin taking the properties seriously. That was the single biggest step toward securing ownership. From that point, the entire focus was on repairing the buildings and getting control of them.
However, the caretaker group nonetheless sued to evict the homesteaders, and a foreclosure case also began against the six-story former squat building in the East Village. My law firm was confident that pressing the caretaker for copies of the building’s financial accounts to corroborate its claim that it had spent all the building’s money on repairs would bear fruit for our side. Just before trial, the caretaker relented, paying in full the tax lien it owed—and the foreclosure was discontinued.

Without the threat of impending foreclosure—and having fleshed out each affordable-housing option for the building—the tenants were finally able to agree on such a program as well as the developer that would implement it.
Under their chosen inclusionary housing program (IHP), the building would be rehabbed and converted into a low-income cooperative. In exchange, the developer would receive certain zoning benefits for on- or off-site use. Prior to (or upon) returning to the rehabbed property, “eligible” tenants (as defined in the temporary-relocation agreement signed by each tenant before relocating) would be offered the chance to buy shares in the cooperative for their respective apartments.
My firm negotiated the various agreements with the caretaker and the developer, obtaining the most favorable terms possible for the tenants and to ensure that they would be entitled to homeownership upon their return. These pacts included a temporary relocation agreement and a relocation rent agreement, among other ancillary arrangements.
By 2021, all homesteaders had moved back in and been given not only keys to the building and their new apartments, but also shares of building ownership and a deed. These residents had become homeowners. I had been their attorney for 16 years—sweating, fighting, rallying, protesting and battling for them every step of the way. But this was all much bigger than me. These residents came to the building as young adults with no money, some still living on what the earth blessed them with. Notably, one 15-year-old, standing at the building on a staircase built by the homesteaders, was discovered by director Larry Clark and cast in the controversial 1995 film Kids as Ruby. Rosario Dawson no longer lives at the building but has worked closely with my firm and me, as well as her family, to make sure it remains properly maintained and protected. In so many ways, this exemplifies the American Dream coming true. A Hollywood ending, you might say.
Actively at the helm of the law firm he built from scratch, Adam Leitman Bailey, Esq. practices residential and commercial real estate law and litigation.
Read the Article Here on Best Lawyers